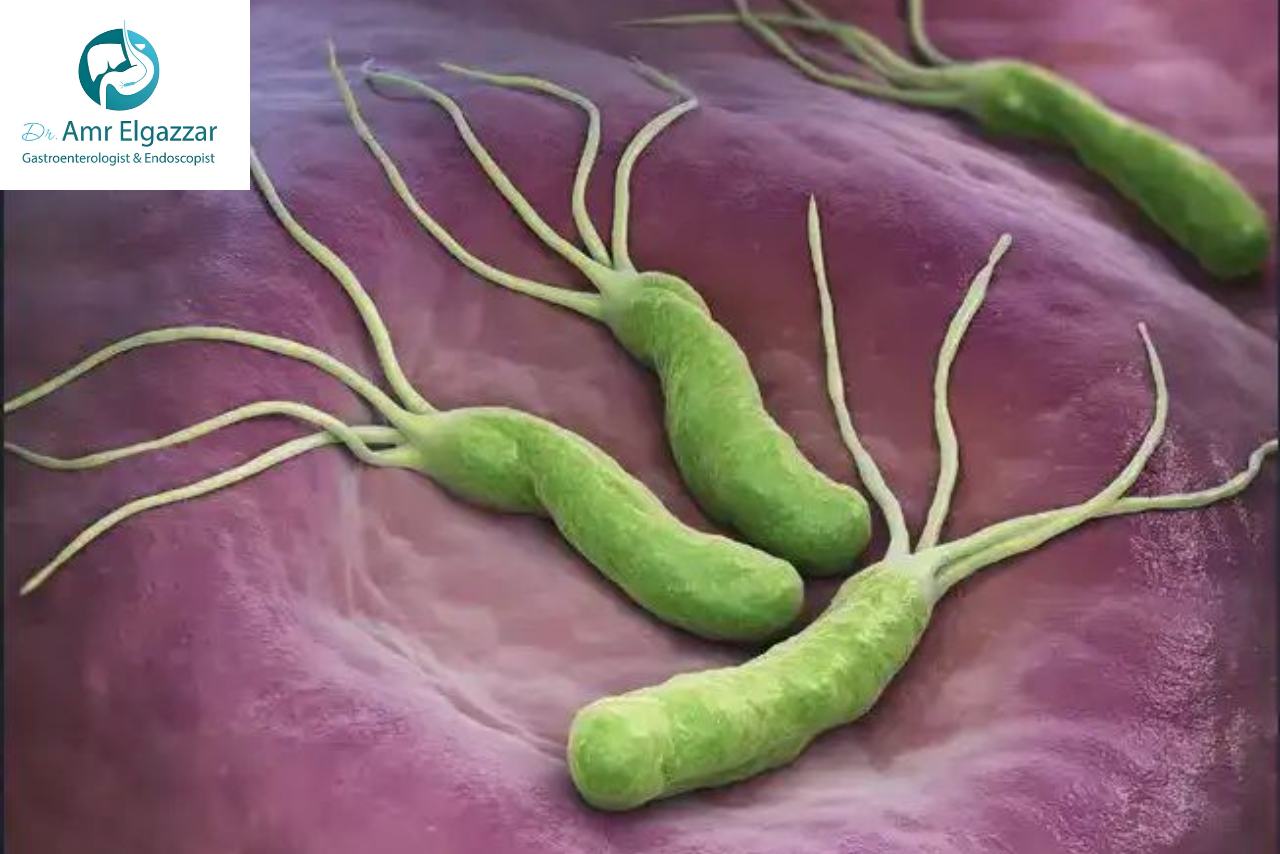
What is Helicobacter pylori?
Helicobacter pylori is a type of bacteria known as H. pylori. It penetrates the lining of the stomach and the upper part of the small intestine, causing ulcers and, in some cases, may lead to stomach cancer. Most people do not realize they are infected with H. pylori because it often causes no noticeable symptoms.
What are the symptoms of H. pylori infection?
If you are infected, you may experience:
-
Bloating
-
Belching
-
Loss of appetite
-
Nausea and vomiting
-
Unexplained weight loss
-
Burning stomach pain, which worsens when hungry
Possible complications of H. pylori infection include:
-
Blood in the stool
-
Breathing difficulties
-
Dizziness or fainting
-
Severe unexplained fatigue
-
Pale skin
-
Severe stomach pain
-
Bleeding in the stomach or intestines, which may appear in vomit or stool and poses serious health risks. Immediate medical attention is advised if this occurs.
H. pylori infection may also increase the risk of stomach cancer, with symptoms including:
-
Abdominal swelling
-
Nausea
-
Loss of appetite
-
Vomiting
-
Unexplained weight loss
Causes and risk factors:
The exact cause of H. pylori infection is unknown, but it can be transmitted through contaminated food or water, or via fecal-oral contact. Poor hygiene practices, such as not washing hands properly after using the bathroom or not cleaning food thoroughly, may contribute. The bacteria produce substances that neutralize stomach acid, making the stomach more vulnerable to damage.
Doctors may recommend treatment, especially if you have family members with stomach ulcers or cancer, as these conditions are linked to H. pylori.
Treatment of H. pylori infection:
-
Medications:
Treatment usually involves a combination of antibiotics along with medications to reduce stomach acid. Commonly prescribed medications include:-
Clarithromycin (antibiotic)
-
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)
-
Metronidazole (antibiotic, taken for 7–14 days)
-
Amoxicillin (antibiotic, taken for 7–14 days)
-
-
Lifestyle and dietary changes:
There is no definitive evidence that diet can prevent H. pylori infection or ulcers. However, spicy foods, alcohol, and smoking can worsen ulcers and delay healing.